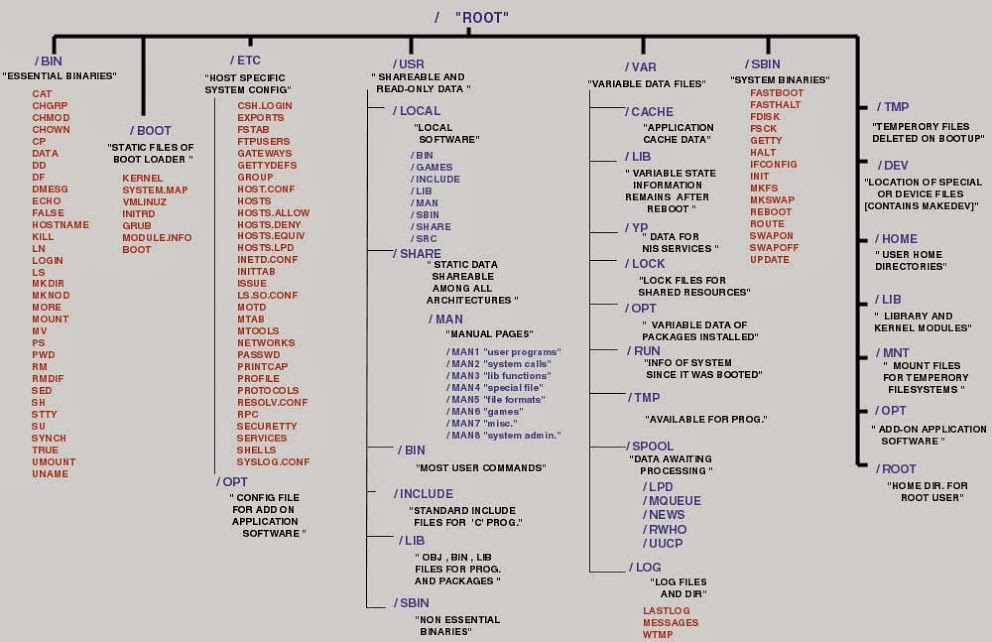
Linux File System
Linux commands:
Navigating the file system
You can think of directory as a folder. Current directory means the folder you are in.
pwd - print working directory (current directory we are in)
Tip: Use --help or -h after a command to get more options and their info.
Note: Everything is case sensitive in linux.

cd [directory address]- change directory = change the current directory
cd .. = change directory backwards (go to the folder before or go back)
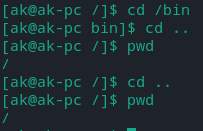
Note: ‘/’ is the lowest you can go.
- ‘/’ is the base(ROOT), it can be use to go to any directory if the whole address is provided like
cd /home/user/Desktop
will take us to the Desktop.
- If you want to go to Music folder from Desktop folder you can type ~/Music/ instead of ../Music/ or /home/user/Music
~ = /home/user
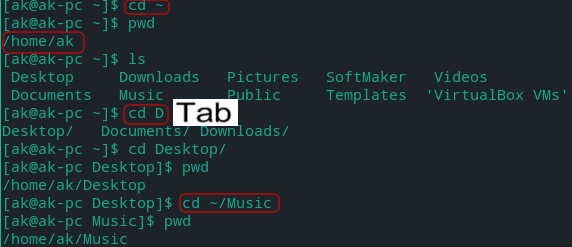
Tip: Use TAB button to auto-complete commands,directory name,file name etc in terminal.
Note: Sometimes terminal won’t know what you’re trying to type because there are multiple matches. Press the Tab key a second time and you’ll see a list of possible matches. Continue typing a few more letters to narrow things down and press Tab again to continue.
ls = list everything in the directory
ls -al = list permissions , details and all content including hidden content (beginning with . or ..)
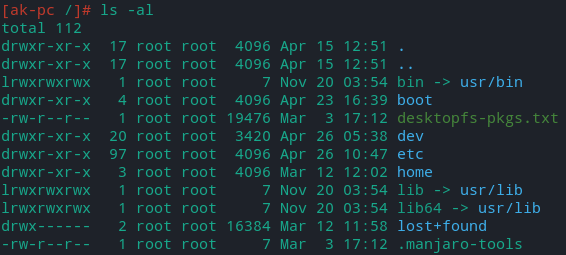
- Color of content will depend on folder,file or permission settings, all of them will be highlighted differently
- Colors are only available to root user
- You can even list files of a folder without event navigating to it.
ls (Directory address)
Ex:
ls /home/user/Desktop
will list files on the Desktop

man [command/program] - To open manual page of a command or program and get more information about it.
Press q to quit man page.
mkdir [folder name] - make new directory = to create a new folder
nano [fil.extension]- to create or edit a text/bash/python etc file
Note: nano needs to be pre-installed.
- extension defines type of file
.txt or blank for text
.sh for shell script
.py for python script
cat [file.extension]- print contents of a text/bash/python etc file
cp [file/folder name] [new location] - copy files and folders
mv [file/folder name] [new location] - move files and folders, can also use it to rename them
mv <file_name> <new_name> - rename a file
rmdir [folder name] - To remove empty folder
rm [file/folder name] - remove files and non-empty folder
sudo - use to perform admin (root user) functions or commands
sudo -s or -i - makes you system admin (give access to root shell) ,after that you do not need to use sudo again and again to perform root actions.
sudo !! - repeat a command with root privilege (add sudo in beginning) without typing it again. [Sudo Bang! Bang!]
ping - to ping a device to probe if it is up
ifconfig - To list and manage network interfaces,IP address and other details
locate [file name] - to locate(find) a file
updatedb - update database used by locate command
- If locate and updatedb are missing install mlocate package.
adduser <new_account_name> - to setup other user accounts
passwd - change user password
Note: A normal user may only change the password for their own account, while the superuser may change the password for any account. passwd also changes the account or associated password validity period.
Note: The user is first prompted for their old password, if one is present. This password is then encrypted and compared against the stored password. The user has only one chance to enter the correct password. The superuser is permitted to bypass this step so that forgotten passwords may be changed.
Tip: UP and DOWN Arrow buttons can be used in terminal to scroll through old commands.